Our Knees and EVOO - Blog # 39
Hi Everyone! Welcome back to another Friday blog. Osteoarthritis (OA) is on the rise in multiple joints, but particularly of the knee. According to the NIH, “knee OA is more important not only for its high prevalence rate compared with other types of OA but also for its presentation at earlier age groups particularly in younger age groups of obese women. The incidence of knee OA increases by age and further increase with longer lifetime and higher average weight of the population.” Today I want to look at what we can do to prevent OA, knee pain and possibly a total knee replacement down the road. So, let’s take a look at what OA really is.
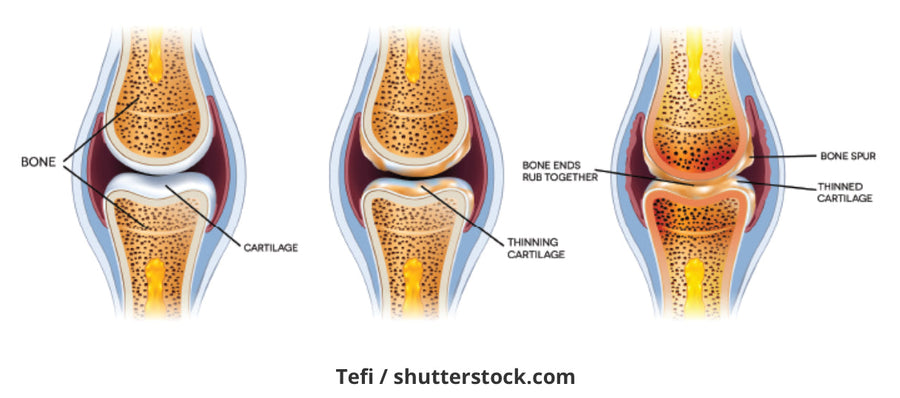
OA is a disease characterized by pain and localized inflammation of the joint with destruction of articular cartilage that leads to loss of function. The joint becomes stiff, swollen, painful, tender with crepitus (gravely sound) and limited mobility. You can't sneak up on anyone because they can hear you coming. It has long been considered a disease that is just 'wear and tear' and mainly affects the cartilage. I've had patients tell me they've rubbed WD-40 on their knees! What really is going on? At a cellular level changes are taking place - molecular derangements begin to occur due to abnormal joint metabolism. As the condition worsens, you begin to have anatomical/physiological derangements of the joint - cartilage degradation and remodeling of subchondral bone as well as inflammation. This results in osteophyte formation or bone spurring, which is quite painful. Why is this happening?
OA displays a “much more complex pathology with inflammatory mediators released by bone, cartilage and synovium. Low-grade inflammation induced by metabolic syndrome, innate immunity and chronic inflammation (‘inflammaging’) are some of the more recent arguments in favour of an inflammatory role in OA and, for the link between inflammation and epigenetic regulation in OA.” In other words, inflammation is the driver! What we choose to eat and how we choose to move our bodies and live our lives is what drives arthritis. If we eat a nutrient-deplete inflammatory diet, sit indoors under synthetic light all day and don't exercise or move, how can our cartilage get all the things it requires to be healthy?
Besides the breakdown of articular cartilage, OA causes changes in the bone and deterioration of the connective tissues that hold the joint together and attach muscle to bone - our ligaments and tendons. Bones have a lot of nerve endings and blood vessels. Direct bone to bone is painful! What causes this breakdown? Most people think of OA as an age-related problem. However, it is happening to us at younger ages due to obesity, chronic low-grade inflammation, low physical activity and poor diet. According to the CDC, OA is the 6th leading cause of debility. It affects your health in a number of ways.

Knee cartilage bears approximately 3 times the body’s weight while performing daily activities,10 times the body’s weight during running and roughly 20 times the body’s weight when participating in jumping. Think of the millions of cycles of mechanical loads our chondrocytes are subjected to in a year! Now, think about adding an abnormal mechanical load to that which can be caused by factors such as obesity, joint instability, cumulative micro-injuries or trauma to the joints from excessive load increase in the activities of daily life - and induce the conversion of healthy cartilage to degenerative joint disease and OA. "Osteoarthritis involves the significant expression of inflammatory cytokines, matrix proteins and proteolytic enzymes. For this reason, anti-inflammatory molecules play a major role in controlling the adverse effects of cartilage homeostatic balance loss. Olive oil, olive leaf extract, curcumin and sanguinarine have been studied as supplements with anti-inflammatory properties. Moreover, chondrocytes undergo senescence and cell death in the presence of oxidative stress. Potential targets involved in this mechanism are counteracted by anti-oxidant molecules like vitamin D and carnosic acid."
A recent study looked at muscle weakness and knee OA. They found that women with weak quadriceps strength resulted in a 47% increase in developing OA of the knee, while weak hamstrings resulted in a 41% increase. “Without strong quadriceps muscles, more stress is placed on the cartilage within the knee, and this has been suggested to induce a degenerative process, wearing down of the cartilage and ultimately osteoarthritis.” The quadriceps muscle in the thigh is able to act as a shock absorber and stabilizer of the knee, relieving stress at the articular surface. Researchers did not find the same results for men, likely due to muscle response to higher body mass index (BMI). When we look at the impact of OA on our lives, it is no surprise that it affects multiple facets.

Obesity is a significant risk factor on its own. According to Johns Hopkins - Overweight women have nearly 4 times the risk of knee OA; for overweight men the risk is 5 times greater.

As we can see from the map, we Texans tend toward obesity. Can we blame it on the 100 degree summer heat?….😂 I can’t go outside right now. Too hot.
What can we do to prevent knee OA?
- Lose weight (if you are overweight) - According to the CDC, “a woman of normal height, for every 11 lb weight loss (approximately 2 BMI units), the risk of knee OA dropped > 50%. Conversely, a comparable weight gain was associated with an increased risk of later developing knee OA (odds ratio 1.28 for a 2 BMI weight gain).”
- Exercise - Build muscle particularly in quadriceps and hamstrings to improve muscle power, circulation and preserve and repair cartilage. Increasing strength around the knee with the appropriate exercises decreases stress to the articular cartilage. High intensity running, plyometrics and high impact aerobic exercise can be damaging to the articular cartilage. Instead, choose speed-walking, resistance training, yoga, rebounding and cycling. Understand that maintaining full range of motion of your joints is imperative to the health of your cartilage. It is through movement that your articular cartilage gets oxygen and gets rid of waste to help prevent deterioration. Stretch daily. Walk daily. Move daily. This is one reason YOGA can be so good for us. Recent studies “confirm the importance of the physical activity in conjunction with extra-virgin olive oil diet in medical therapy to prevent osteoarthritis disease in order to preserve the articular cartilage and then the entire joint.” In mice, studies demonstrate that it is the combination of light/moderate treadmill exercise + EVOO offer the best protection to our articular cartilage to date!!!
- Vitamin D3 - really a hormone and powerful anti-inflammatory. There is a receptor on every cell in the human body. Get plenty of sunshine to synthesize vitamin D and supplement to achieve optimal levels of 70-100 on blood work.
- Grounding - put your bare feet on the damp cool grass (not sprayed with pesticides and herbicides) - the earth is a giant magnet. We literally discharge into the earth and repolarize our cells decreasing inflammation. If you can ground in the ocean - all the better due to the conductivity of sea water.
- Sleep - guard your sleep. This is when your body does repair. Don't eat 3 hours before bedtime. Aim for 8-9 hours of quality sleep from 9pm-3am for maximal brain cleansing and abnormal protein clearing to occur.
- Eat real food that grows in the ground or feeds on the grass. Eat organic to eliminate as much glyphosate as possible.
- EVOO - “olive oil and its derivatives are potential therapeutic agents for inflammatory diseases like OA.” The polyphenols in EVOO exert potent anti-inflammatory effects, alleviate pain and have chondroprotective properties. Oleocanthal and oleuropein - two powerful polyphenols in EVOO - are potent analgesics that act similar to ibuprofen to relieve pain in the body, but without any side effects. It mitigates pain so profoundly, many MDs are prescribing it to their patients!! A study in 2017 showed Oleuropein supplementation reduced the level of PGE2(inflammation marker) and collagen-2 (cartilage degradation marker) for OA. In a 2017 study with mice, they transected the ACL in the knee to create injury, which significantly decreased lubricin expression and set off inflammatory markers. The combination of treadmill training along with EVOO reversed this by normalizing the lubricin - an important chondroprotective glycoprotein that serves as a critical boundary lubricant between opposing cartilage surfaces - and interlukin-1 levels! WHAT?!!! "Oral uptake of extra virgin olive oil rich diet has anti-inflammatory effects and suppressed IL-6 expression and upregulated the expression of lubricin in a rat model of ACLT induced OA." The powerful polyphenols in EVOO halt the progression toward OA. To top it all off, Oleocanthal and oleuropein are powerful pain relievers We don’t have to kill ourselves at the gym to get these benefits. Take your EVOO shot and go for a walk!! Done.
So, until next time my friends…Drink, Drizzle, Digest HP-EVOO at least 4T raw daily, - use more for cooking and drizzling onto your food - eat the rainbow of organic or wild-sourced or organic veggies (7-9 C) and low-glycemic fruits (to get the rainbow of gut microbes!) - eat wild-caught, pasture-raised, grass-fed - get plenty of sunshine - supplement magnesium, zinc, vitamin D3 + K2 - get your trace minerals and electrolytes with good sea salt - Celtic is hand-harvested and Himalayan was formed before plastics - eat foods high in lutein - drink your body weight in oz of water - get a good pre/probiotic - consume digestible and indigestible fiber for your gut microbes - adaptogens (such as mushrooms) and methylation donors (kale, beets, spinach, cruciferous, lion’s mane…), marjoram, rosemary, oregano, parsley and other herbs to detox, enhance overall health and reverse aging and disease - exercise your body and mind - add a few minutes of mindful meditation and breathing exercises to your day to combat stress - take a hot Epsom salt bath and follow with a cold shower/ice plunge - practice “earthing” as an anti-inflammatory - remove EMF (electromagnetic frequency) devices and blue light - use IR (infrared) from incandescent lighting, non-toxic candle or light a fire to enhance sleep and...turn off the light!! #HP-EVOO
This blog is intended for informational purposes only. Discuss strategies with your Healthcare Practitioner.







Comments (2)
Wow, such valuable information you have shared about the health benefits from having EVOO in one’s diet in combination with all of the other daily requirements needed to insure a healthy life. Thanks. I only wish I had been aware of this at an earlier age. However, at the age of 81 , I feel it’s not too late to start living a healthier love style. Thanks and keep getting this message out to the public. 💘
I take my EVOO every morning with pineapple juice and have found that it helps me in multiple ways. At the age of 86 I feel healthy and happy with plenty of energy to do most things I enjoy, especially walking. I’m very thankful my knees still allow me to do that, and believe the EVOO is a contributing factor. Thank you for the many hours of research you do to help your expanding community.